mean value theorem
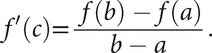
This can be equivalently expressed as:there is a point C on the graph of f where the tangent is parallel to the line segment joining A(a,f(a)) to B(b,f(b)). If A, with coordinates (a, f(a)), and B, with coordinates (b, f(b)), are the points on the graph corresponding to the end‐points of the interval, there must be a point C on the graph between A and B at which the tangent is parallel to the chord AB.
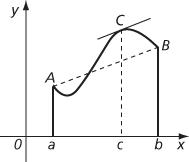
Mean gradient achieved at C
Rolle's Theorem is a special case of the mean value theorem. Taylor's Theorem is an extension of the mean value theorem. The mean value theorem has two immediate corollaries:
- distribution
- distribution function
- distribution‐free methods
- distributive
- div
- diverge
- divergence
- divergence theorem
- divides
- divisible
- division
- division
- division algebra
- Division Algorithm
- division ring
- divisor
- divisor function
- divisor of zero
- dodecagon
- dodecahedron
- Dodgson, Charles Lutwidge
- domain
- domain
- domain
- dominated convergence theorem