Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics which studies the possible outcomes of given events together with their relativelikelihoods and distributions. In common usage, the word ``probability'' is used to mean the chance that a particular event(or set of events) will occur expressed on a linear scale from 0 (impossibility) to 1 (certainty), also expressed as aPercentage between 0 and 100%. The analysis of events governed by probability is called Statistics.
There are several competing interpretations of the actual ``meaning'' of probabilities. Frequentists view probability simplyas a measure of the frequency of outcomes (the more conventional interpretation), while Bayesianstreat probability more subjectively as a statistical procedure which endeavors to estimate parameters of an underlyingdistribution based on the observed distribution.
A properly normalized function which assigns a probability ``density'' to each possible outcome within some interval is calleda Probability Function, and its cumulative value (integral for a continuous distribution or sum for a discrete distribution) is called a Distribution Function.
Probabilities are defined to obey certain assumptions, called the Probability Axioms. Let a Sample Space containthe Union (![]() ) of all possible events
) of all possible events ![]() , so
, so
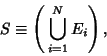 | (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
where
Let ![]() denote the Conditional Probability of
denote the Conditional Probability of ![]() given that
given that ![]() has already occurred, then
has already occurred, then
| (5) | |||
| (6) | |||
| (7) | |||
| (8) | |||
| (9) | |||
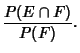 | (10) |
A very important result states that
| (11) |
| (12) |
- Hyperspace
- Hypersphere
- Hypersphere Packing
- Hypervolume
- Hypocycloid
- Hypocycloid--3-Cusped
- Hypocycloid--4-Cusped
- Hypocycloid Evolute
- Hypocycloid Involute
- Hypocycloid Pedal Curve
- Hypoellipse
- Hypotenuse
- Hypothesis
- Hypothesis Testing
- Hypotrochoid
- Hypotrochoid Evolute
- Hyzer's Illusion
- Hénon Attractor
- Hénon-Heiles Equation
- Hénon Map
- Hölder Condition
- Hölder Integral Inequality
- Hölder Sum Inequality
- i
- I