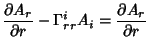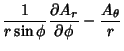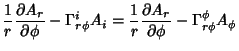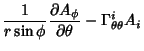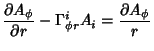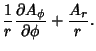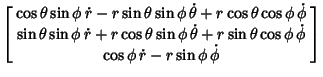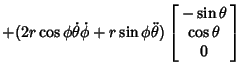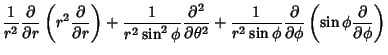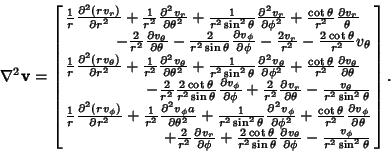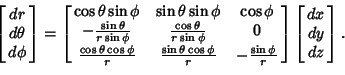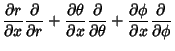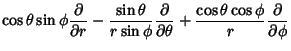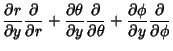| 释义 |
Spherical CoordinatesA system of Curvilinear Coordinates which is natural for describing positions on a Sphere or Spheroid. Define 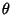 to be the azimuthal Angle in the to be the azimuthal Angle in the  -Plane from the x-Axis with -Plane from the x-Axis with  (denoted (denoted  when referred to as the Longitude), when referred to as the Longitude),  to be the polar Angle from the z-Axiswith to be the polar Angle from the z-Axiswith  (Colatitude, equal to (Colatitude, equal to  where where  is the Latitude), and is the Latitude), and 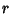 tobe distance (Radius) from a point to the Origin. tobe distance (Radius) from a point to the Origin.
Unfortunately, the convention in which the symbols 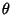 and and  are reversed is frequently used, especially in physics,leading to unnecessary confusion. The symbol are reversed is frequently used, especially in physics,leading to unnecessary confusion. The symbol 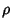 is sometimes also used in place of is sometimes also used in place of 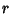 . Arfken (1985) uses . Arfken (1985) uses 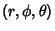 , whereas Beyer (1987) uses , whereas Beyer (1987) uses  . Be very careful when consulting the literature. . Be very careful when consulting the literature.
In this work, the symbols for the azimuthal, polar, and radial coordinates are taken as 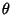 , ,  , and , and 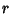 ,respectively. Note that this definition provides a logical extension of the usual Polar Coordinates notation, with ,respectively. Note that this definition provides a logical extension of the usual Polar Coordinates notation, with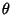 remaining the Angle in the remaining the Angle in the  -Plane and -Plane and  becoming the Angle out of the Plane. becoming the Angle out of the Plane.
where 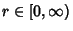 , , 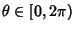 , and , and  . In terms of Cartesian Coordinates, . In terms of Cartesian Coordinates,
The Scale Factors are
so the Metric Coefficients are
The Line Element is
 | (13) |
 | (14) |
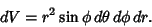 | (15) |
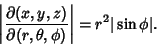 | (16) |
The Position Vector is
 | (17) |
Derivatives of the Unit Vectors are
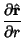 |  |  | (21) |  |  |  | (22) | 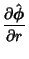 |  |  | (23) |  |  | 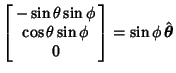 | (24) |  |  |  | (25) |  |  |  | (26) |  |  | 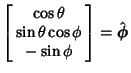 | (27) |  |  |  | (28) |  |  |  | (29) |
The Gradient is
 | (30) |
Now, since the Connection Coefficients are given by , ,
The Divergence is or, in Vector notation,
The Covariant Derivatives are given by
 | (42) |
 |  | 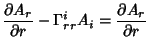 | (43) | 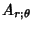 |  |  | | | |  | 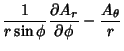 | (44) | 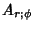 |  | 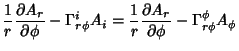 | | | |  |  | (45) |  |  |  | (46) |  |  | 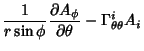 | | | |  | 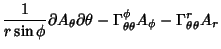 | | | |  |  | (47) | 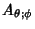 |  |  | (48) | 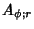 |  | 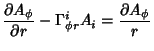 | (49) | 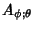 |  |  | | | |  |  | (50) |  |  |  | | | |  | 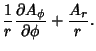 | (51) |
The Commutation Coefficients are given by
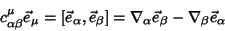 | (52) |
 | (53) |
 , where , where  . .
 | (54) |
 , ,  . .
 | (55) |
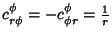 . .
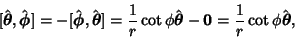 | (56) |
 | (57) |
Time derivatives of the Position Vector are
The Speed is therefore given by
 | (62) |
Plugging these in gives
but
so
Time Derivatives of the Unit Vectors are
The Curl is 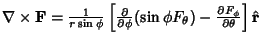 | |  | | | (72) |
The Laplacian is
The vector Laplacian is
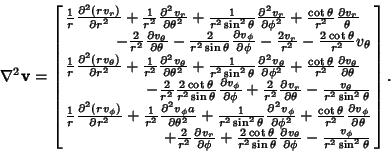 | (74) |
To express Partial Derivatives with respect to Cartesian axes in terms of PartialDerivatives of the spherical coordinates,
Upon inversion, the result is
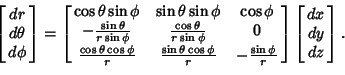 | (77) |
(Gasiorowicz 1974, pp. 167-168).
The Helmholtz Differential Equation is separable in spherical coordinates. See also Colatitude, Great Circle, Helmholtz Differential Equation--Spherical Coordinates, Latitude, Longitude, Oblate Spheroidal Coordinates,Prolate Spheroidal Coordinates
References
Arfken, G. ``Spherical Polar Coordinates.'' §2.5 in Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 102-111, 1985.Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 28th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p. 212, 1987. Gasiorowicz, S. Quantum Physics. New York: Wiley, 1974. Morse, P. M. and Feshbach, H. Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York: McGraw-Hill, p. 658, 1953.
|

![]() to be the azimuthal Angle in the
to be the azimuthal Angle in the ![]() -Plane from the x-Axis with
-Plane from the x-Axis with ![]() (denoted
(denoted ![]() when referred to as the Longitude),
when referred to as the Longitude), ![]() to be the polar Angle from the z-Axiswith
to be the polar Angle from the z-Axiswith ![]() (Colatitude, equal to
(Colatitude, equal to ![]() where
where ![]() is the Latitude), and
is the Latitude), and ![]() tobe distance (Radius) from a point to the Origin.
tobe distance (Radius) from a point to the Origin.![]() and
and ![]() are reversed is frequently used, especially in physics,leading to unnecessary confusion. The symbol
are reversed is frequently used, especially in physics,leading to unnecessary confusion. The symbol ![]() is sometimes also used in place of
is sometimes also used in place of ![]() . Arfken (1985) uses
. Arfken (1985) uses ![]() , whereas Beyer (1987) uses
, whereas Beyer (1987) uses ![]() . Be very careful when consulting the literature.
. Be very careful when consulting the literature.![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() ,respectively. Note that this definition provides a logical extension of the usual Polar Coordinates notation, with
,respectively. Note that this definition provides a logical extension of the usual Polar Coordinates notation, with![]() remaining the Angle in the
remaining the Angle in the ![]() -Plane and
-Plane and ![]() becoming the Angle out of the Plane.
becoming the Angle out of the Plane.

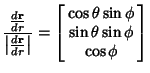
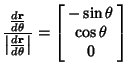

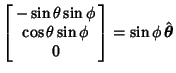


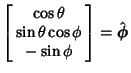

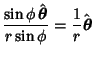


![]() ,
,