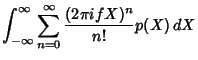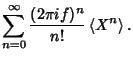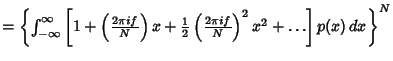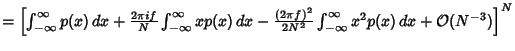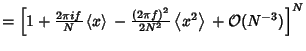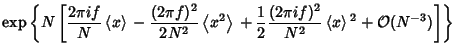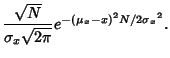| 释义 |
Central Limit TheoremLet 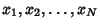 be a set of be a set of  Independent random variates and each Independent random variates and each  have an arbitrary probability distribution have an arbitrary probability distribution  with Mean with Mean  and a finite Variance and a finite Variance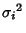 . Then the normal form variate . Then the normal form variate
 | (1) |
 and Variance and Variance  . If conversion to normal form is not performed, then thevariate . If conversion to normal form is not performed, then thevariate
 | (2) |
 and and  . To provethis, consider the Inverse Fourier Transform of . To provethis, consider the Inverse Fourier Transform of  . .
Now write | |  | | | (4) |
so we haveNow expand
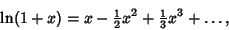 | (6) |
since
Taking the Fourier Transform,
This is of the form
 | (11) |
 and and  . But, fromAbramowitz and Stegun (1972, p. 302, equation 7.4.6), . But, fromAbramowitz and Stegun (1972, p. 302, equation 7.4.6),
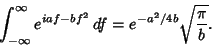 | (12) |
But  and and  , so , so
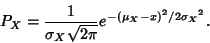 | (14) |
The ``fuzzy'' central limit theorem says that data which are influenced by many small and unrelated random effects areapproximately Normally Distributed. See also Lindeberg Condition, Lindeberg-Feller Central Limit Theorem, Lyapunov Condition
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.). Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing. New York: Dover, 1972.Spiegel, M. R. Theory and Problems of Probability and Statistics. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 112-113, 1992. Zabell, S. L. ``Alan Turing and the Central Limit Theorem.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 102, 483-494, 1995.
|
![]() be a set of
be a set of ![]() Independent random variates and each
Independent random variates and each ![]() have an arbitrary probability distribution
have an arbitrary probability distribution ![]() with Mean
with Mean ![]() and a finite Variance
and a finite Variance![]() . Then the normal form variate
. Then the normal form variate