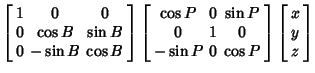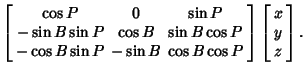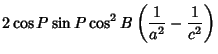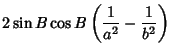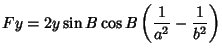| 释义 |
Oblate SpheroidA ``squashed'' Spheroid for which the equatorial radius  is greater than the polar radius is greater than the polar radius 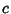 , so , so 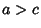 . Tofirst approximation, the shape assumed by a rotating fluid (including the Earth, . Tofirst approximation, the shape assumed by a rotating fluid (including the Earth,  which is ``fluid'' overastronomical time scales) is an oblate spheroid. The oblate spheroid can be specified parametrically by the usualSpheroid equations (for a Spheroid with z-Axis as the symmetry axis), which is ``fluid'' overastronomical time scales) is an oblate spheroid. The oblate spheroid can be specified parametrically by the usualSpheroid equations (for a Spheroid with z-Axis as the symmetry axis),
with 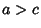 , ,  , and , and 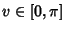 . Its Cartesian equation is . Its Cartesian equation is
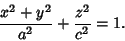 | (4) |
The Ellipticity of an oblate spheroid is defined by
 | (5) |
 | (6) |
 | (7) |
 . .
The Surface Area and Volume of an oblate spheroid are
An oblate spheroid with its origin at a Focus has equation
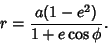 | (10) |
Define  and expand up to Powers of and expand up to Powers of 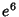 , ,
Expanding 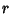 in Powers of Ellipticity to in Powers of Ellipticity to 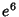 therefore yields therefore yields
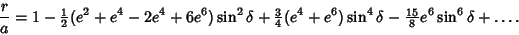 | (14) |
The Ellipticity may also be expressed in terms of the Oblateness (also called Flattening), denoted or or 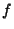 . .
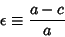 | (16) |
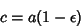 | (17) |
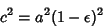 | (18) |
 | (19) |
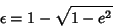 | (20) |
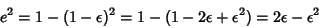 | (21) |
 | (22) |
 and expand up to Powers of and expand up to Powers of 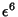
Expanding 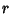 in Powers of the Oblateness to in Powers of the Oblateness to  yields yields
 | (26) |
To find the projection of an oblate spheroid onto a Plane, set up a coordinate system such that the z-Axis istowards the observer, and the 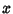 -axis is in the Plane of the page. The equation for an oblate spheroid is -axis is in the Plane of the page. The equation for an oblate spheroid is
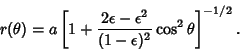 | (28) |
 | (29) |
 . Then . Then
 | (30) |
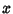 -axis by an Angle -axis by an Angle 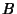 so that the new symmetry axes for the spheroid are so that the new symmetry axes for the spheroid are  , , 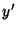 , and , and  . The projected height of a point in the . The projected height of a point in the  Plane on the Plane on the 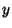 -axis is -axis is
To find the highest projected point,
 | (32) |
 | (33) |
Plugging (34) into (33),
 | (35) |
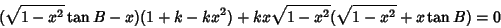 | (36) |
 | |  | (37) |
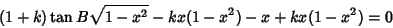 | (38) |
 | (39) |
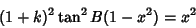 | (40) |
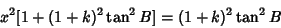 | (41) |
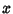 in terms of in terms of 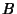 and and  , ,
 | (42) |
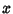 , ,
Now re-express  in terms of in terms of  and and 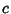 , using , using  , ,
so
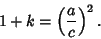 | (45) |
We wish to find the equation for a spheroid which has been rotated about the 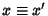 -axis by Angle -axis by Angle 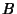 , then the , then the -axis by Angle -axis by Angle 
Now, in the original coordinates  , the spheroid is given by the equation , the spheroid is given by the equation
 | (48) |
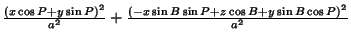 | |  | (49) |
Collecting Coefficients,
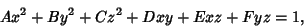 | (50) |
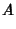 |  |  | (51) |  |  |  | (52) | 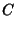 |  |  | (53) |  |  |  | | | |  | 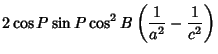 | (54) | 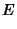 |  |  | (55) | 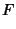 |  |  | (56) |
If we are interested in computing  , the radial distance from the symmetry axis of the spheroid ( , the radial distance from the symmetry axis of the spheroid (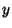 ) corresponding toa point ) corresponding toa point
 | (57) |
 can now be computed using the quadratic equation when can now be computed using the quadratic equation when  is given, is given,
 | (60) |
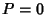 , then we have , then we have  and and 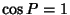 , so (51) to (56) and (58) to (59) become , so (51) to (56) and (58) to (59) become
 |  |  | (61) |  |  |  | (62) |  |  |  | (63) |  |  | 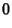 | (64) | 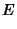 |  | 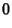 | (65) | 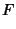 |  | 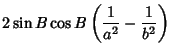 | (66) |  |  | 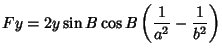 | (67) |  |  | 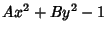 | | | |  |  | (68) |
See also Darwin-de Sitter Spheroid, Ellipsoid, Oblate Spheroidal Coordinates, Prolate Spheroid,Sphere, Spheroid
References
Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 28th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p. 131, 1987.
|
![]() is greater than the polar radius
is greater than the polar radius ![]() , so
, so ![]() . Tofirst approximation, the shape assumed by a rotating fluid (including the Earth,
. Tofirst approximation, the shape assumed by a rotating fluid (including the Earth, ![]() which is ``fluid'' overastronomical time scales) is an oblate spheroid. The oblate spheroid can be specified parametrically by the usualSpheroid equations (for a Spheroid with z-Axis as the symmetry axis),
which is ``fluid'' overastronomical time scales) is an oblate spheroid. The oblate spheroid can be specified parametrically by the usualSpheroid equations (for a Spheroid with z-Axis as the symmetry axis),

![]() and expand up to Powers of
and expand up to Powers of ![]() ,
,
![]() -axis is in the Plane of the page. The equation for an oblate spheroid is
-axis is in the Plane of the page. The equation for an oblate spheroid is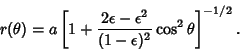




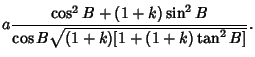


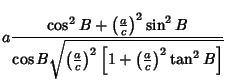
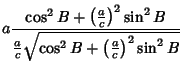


![]() -axis by Angle
-axis by Angle ![]() , then the
, then the![]() -axis by Angle
-axis by Angle ![]()