| 释义 |
DiceA die (plural ``dice'') is a Solid with markings on each of its faces. The faces are usually all the same shape,making Platonic Solids and Archimedean Solid Duals the obviouschoices. The die can be ``rolled'' by throwing it in the air and allowing it to come to rest on one of its faces. Dice areused in many games of chance as a way of picking Random Numbers on which to bet, and are used inboard or role-playing games to determine the number of spaces to move, results of a conflict, etc. A Coin can be viewed as a degenerate 2-sided case of a die.
The most common type of die is a six-sided Cube with the numbers 1-6 placed on the faces. The value of the roll isindicated by the number of ``spots'' showing on the top. For the six-sided die, opposite faces are arranged to always sumto seven. This gives two possible Mirror Image arrangements in which the numbers 1, 2, and 3 may be arranged in aclockwise or counterclockwise order about a corner. Commercial dice may, in fact, have either orientation. Theillustrations below show 6-sided dice with counterclockwise and clockwise arrangements, respectively. 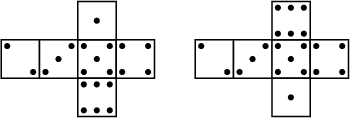
The Cube has the nice property that there is an upward-pointing face opposite the bottom face from which the value ofthe ``roll'' can easily be read. This would not be true, for instance, for a Tetrahedral die, whichwould have to be picked up and turned over to reveal the number underneath (although it could be determined by noting whichnumber 1-4 was not visible on one of the upper three faces). The arrangement of spots 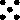 corresponding to a roll of 5 on a six-sided die is called the Quincunx. There are also special names for certain rollsof two six-sided dice: two 1s are called Snake Eyes and two 6s are called Boxcars. corresponding to a roll of 5 on a six-sided die is called the Quincunx. There are also special names for certain rollsof two six-sided dice: two 1s are called Snake Eyes and two 6s are called Boxcars.
Shapes of dice other than the usual 6-sided Cube are commercially available from companies such as Dice & Games,Ltd.
Diaconis and Keller (1989) show that there exist ``fair'' dice other than the usual Platonic Solidsand duals of the Archimedean Solids, where a fair die is one for which its symmetry group actstransitively on its faces. However, they did not explicitly provide any examples.
The probability of obtaining  points (a roll of points (a roll of 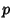 ) on ) on  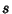 -sided dice can be computed as follows. The number ofways in which -sided dice can be computed as follows. The number ofways in which 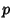 can be obtained is the Coefficient of can be obtained is the Coefficient of 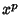 in in
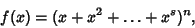 | (1) |
 can be written as a Multinomial Series can be written as a Multinomial Series
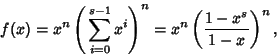 | (2) |
 is the Coefficient of is the Coefficient of 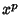 in in
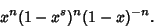 | (3) |
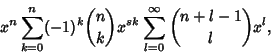 | (4) |
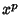 , include all terms with , include all terms with
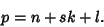 | (5) |
 is therefore is therefore
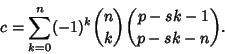 | (6) |
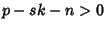 only when only when 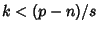 , so the other terms do not contribute. Furthermore, , so the other terms do not contribute. Furthermore,
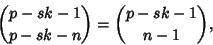 | (7) |
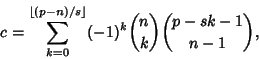 | (8) |
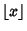 is the Floor Function, and is the Floor Function, and
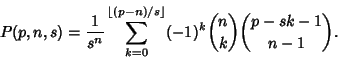 | (9) |
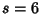 . For . For 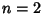 six-sided dice, six-sided dice,
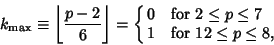 | (10) |
The most common roll is therefore seen to be a 7, with probability 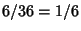 , and the least common rolls are 2 and 12, bothwith probability 1/36. , and the least common rolls are 2 and 12, bothwith probability 1/36.
For  six-sided dice, six-sided dice,
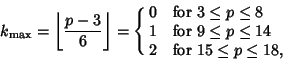 | (12) |
For three six-sided dice, the most common rolls are 10 and 11, both with probability 1/8; and the least common rolls are 3and 18, both with probability 1/216.
For four six-sided dice, the most common roll is 14, with probability 73/648; and the least common rolls are 4 and 24, bothwith probability 1/1296.
In general, the likeliest roll  for for  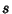 -sided dice is given by -sided dice is given by
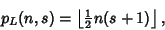 | (14) |
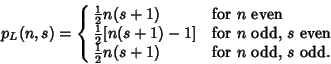 | (15) |
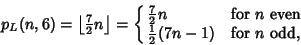 | (16) |
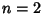 , 3, ... (Sloane's A030123) dice. The probabilities correspondingto the most likely rolls can be computed by plugging , 3, ... (Sloane's A030123) dice. The probabilities correspondingto the most likely rolls can be computed by plugging 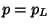 into the general formula together with into the general formula together with
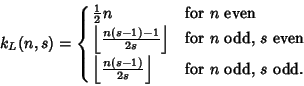 | (17) |
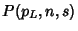 does not have a simple closed-form expression in terms of does not have a simple closed-form expression in terms of 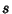 and and  . However, theprobabilities of obtaining the likeliest roll totals can be found explicitly for a particular . However, theprobabilities of obtaining the likeliest roll totals can be found explicitly for a particular 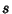 . For . For  6-sided dice,the probabilities are 1/6, 1/8, 73/648, 65/648, 361/3888, 24017/279936, 7553/93312, ... for 6-sided dice,the probabilities are 1/6, 1/8, 73/648, 65/648, 361/3888, 24017/279936, 7553/93312, ... for 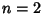 , 3, .... , 3, ....
The probabilities for obtaining a given total using  6-sided dice are shown above for 6-sided dice are shown above for 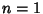 , 2, 3, and 4 dice. Theycan be seen to approach a Gaussian Distribution as the number of dice is increased. , 2, 3, and 4 dice. Theycan be seen to approach a Gaussian Distribution as the number of dice is increased. See also Boxcars, Coin Tossing, Craps, de Mere's Problem, Efron's Dice, Poker,Quincunx, Sicherman Dice, Snake Eyes
References
Diaconis, P. and Keller, J. B. ``Fair Dice.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 96, 337-339, 1989.Dice & Games, Ltd. ``Dice & Games Hobby Games Accessories.'' http://www.dice.co.uk/hob.htm. Gardner, M. ``Dice.'' Ch. 18 in Mathematical Magic Show: More Puzzles, Games, Diversions, Illusions and Other Mathematical Sleight-of-Mind from Scientific American. New York: Vintage, pp. 251-262, 1978. Robertson, L. C.; Shortt, R. M.; Landry, S. G. ``Dice with Fair Sums.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 95, 316-328, 1988. Sloane, N. J. A. Sequence A030123in ``The On-Line Version of the Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.''http://www.research.att.com/~njas/sequences/eisonline.html.
|

![]() corresponding to a roll of 5 on a six-sided die is called the Quincunx. There are also special names for certain rollsof two six-sided dice: two 1s are called Snake Eyes and two 6s are called Boxcars.
corresponding to a roll of 5 on a six-sided die is called the Quincunx. There are also special names for certain rollsof two six-sided dice: two 1s are called Snake Eyes and two 6s are called Boxcars.![]()
![]() points (a roll of
points (a roll of ![]() ) on
) on ![]()
![]() -sided dice can be computed as follows. The number ofways in which
-sided dice can be computed as follows. The number ofways in which ![]() can be obtained is the Coefficient of
can be obtained is the Coefficient of ![]() in
in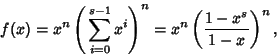
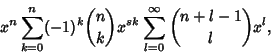
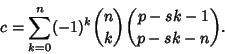
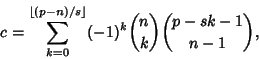
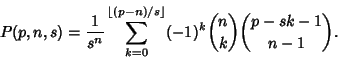
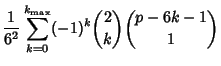
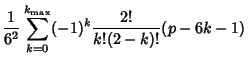
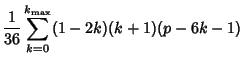
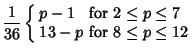
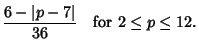
![]() six-sided dice,
six-sided dice,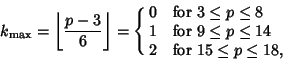
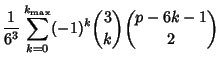
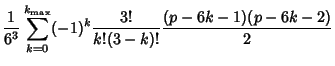
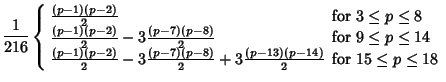
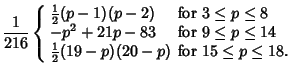
![]() for
for ![]()
![]() -sided dice is given by
-sided dice is given by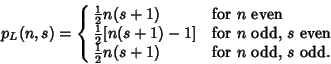
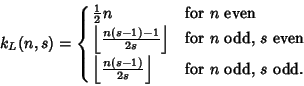
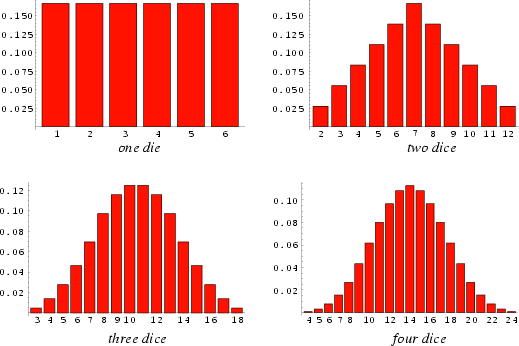
![]() 6-sided dice are shown above for
6-sided dice are shown above for ![]() , 2, 3, and 4 dice. Theycan be seen to approach a Gaussian Distribution as the number of dice is increased.
, 2, 3, and 4 dice. Theycan be seen to approach a Gaussian Distribution as the number of dice is increased.