p-adic Number
A ![]() -adic number is an extension of the Field of Rational Numbers such thatCongruences Modulo Powers of a fixed Prime
-adic number is an extension of the Field of Rational Numbers such thatCongruences Modulo Powers of a fixed Prime ![]() are related to proximity inthe so called ``
are related to proximity inthe so called ``![]() -adic metric.''
-adic metric.''
Any Nonzero Rational Number ![]() can be represented by
can be represented by
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
As an example, consider the Fraction
| (4) |
| (5) | |||
| (6) | |||
| (7) | |||
| (8) | |||
| (9) |
The ![]() -adic absolute value satisfies the relations
-adic absolute value satisfies the relations
- 1.
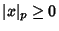 for all
for all  ,
, - 2.
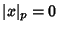 Iff
Iff  ,
, - 3.
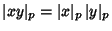 for all
for all 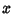 and
and 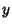 ,
, - 4.
 for all
for all 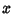 and
and 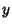 (the Triangle Inequality), and
(the Triangle Inequality), and - 5.
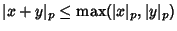 for all
for all 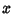 and
and 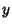 (the Strong Triangle Inequality).
(the Strong Triangle Inequality).
The ![]() -adics were probably first introduced by Hensel in 1902 in a paper which was concerned with the development of algebraicnumbers in Power Series.
-adics were probably first introduced by Hensel in 1902 in a paper which was concerned with the development of algebraicnumbers in Power Series. ![]() -adic numbers were then generalized to Valuations by Kürschák in1913. In the early 1920s, Hasse formulated the Local-Global Principle (now usually called the Hasse Principle),which is one of the chief applications of Local Field theory. Skolem's
-adic numbers were then generalized to Valuations by Kürschák in1913. In the early 1920s, Hasse formulated the Local-Global Principle (now usually called the Hasse Principle),which is one of the chief applications of Local Field theory. Skolem's ![]() -adic method, which is used in attackingcertain Diophantine Equations, is another powerful application of
-adic method, which is used in attackingcertain Diophantine Equations, is another powerful application of ![]() -adic numbers. Anotherapplication is the theorem that the Harmonic Numbers
-adic numbers. Anotherapplication is the theorem that the Harmonic Numbers ![]() are never Integers(except for
are never Integers(except for ![]() ). A similar application is the proof of the von Staudt-Clausen Theorem using the
). A similar application is the proof of the von Staudt-Clausen Theorem using the ![]() -adic valuation,although the technical details are somewhat difficult. Yet another application is provided by the Mahler-Lech Theorem.
-adic valuation,although the technical details are somewhat difficult. Yet another application is provided by the Mahler-Lech Theorem.
Every Rational ![]() has an ``essentially'' unique
has an ``essentially'' unique ![]() -adic expansion (``essentially'' since zeroterms can always be added at the beginning)
-adic expansion (``essentially'' since zeroterms can always be added at the beginning)
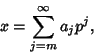 | (10) |
| (11) |
| (12) |
| (13) |
| (14) |
The ![]() -adic valuation on
-adic valuation on ![]() gives rise to the
gives rise to the ![]() -adic metric
-adic metric
| (15) |
Just as the Real Numbers are the completion of the Rationals ![]() withrespect to the usual absolute valuation
withrespect to the usual absolute valuation ![]() , the
, the ![]() -adic numbers are the completion of
-adic numbers are the completion of ![]() with respect to the
with respect to the![]() -adic valuation
-adic valuation ![]() . The
. The ![]() -adic numbers are useful in solving Diophantine Equations.For example, the equation
-adic numbers are useful in solving Diophantine Equations.For example, the equation ![]() can easily be shown to have no solutions in the field of 2-adic numbers (we simply take thevaluation of both sides). Because the 2-adic numbers contain the rationals as a subset, we can immediately see that theequation has no solutions in the Rationals. So we have an immediate proof of the irrationality of
can easily be shown to have no solutions in the field of 2-adic numbers (we simply take thevaluation of both sides). Because the 2-adic numbers contain the rationals as a subset, we can immediately see that theequation has no solutions in the Rationals. So we have an immediate proof of the irrationality of![]() .
.
This is a common argument that is used in solving these types of equations: in order to show that an equation has no solutionsin ![]() , we show that it has no solutions in a Field Extension. For another example, consider
, we show that it has no solutions in a Field Extension. For another example, consider ![]() . Thisequation has no solutions in
. Thisequation has no solutions in ![]() because it has no solutions in the reals
because it has no solutions in the reals ![]() , and
, and ![]() is a subset of
is a subset of![]() .
.
Now consider the converse. Suppose we have an equation that does have solutions in ![]() and in all the
and in all the ![]() . Can we conclude that the equation has a solution in
. Can we conclude that the equation has a solution in ![]() ? Unfortunately, in general, the answer is no, but thereare classes of equations for which the answer is yes. Such equations are said to satisfy the Hasse Principle.
? Unfortunately, in general, the answer is no, but thereare classes of equations for which the answer is yes. Such equations are said to satisfy the Hasse Principle.
References
Burger, E. B. and Struppeck, T. ``Does Cassels, J. W. S. and Scott, J. W. Local Fields. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1986. Gouvêa, F. Q. Koblitz, N. Mahler, K. ![]() P-adic Numbers
P-adic Numbers![]() Really Converge? Infinite Series and
Really Converge? Infinite Series and ![]() -adic Analysis.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 103, 565-577, 1996.
-adic Analysis.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 103, 565-577, 1996.![]() -adic Numbers: An Introduction, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1997.
-adic Numbers: An Introduction, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1997.![]() -adic Numbers,
-adic Numbers, ![]() -adic Analysis, and Zeta-Functions, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1984.
-adic Analysis, and Zeta-Functions, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1984.![]() -adic Numbers and Their Functions, 2nd ed. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1981.
-adic Numbers and Their Functions, 2nd ed. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1981.
- Handkerchief Surface
- Handle
- Handlebody
- Hankel Function
- Hankel Function of the First Kind
- Hankel Function of the Second Kind
- Hankel Matrix
- Hankel's Integral
- Hankel Transform
- Hann Function
- Hanning Function
- Hanoi Graph
- Hanoi Towers
- Hansen-Bessel Formula
- Hansen Chain
- Hansen Number
- Hansen's Problem
- Happy Number
- Harada-Norton Group
- Harary Graph
- Hard Hexagon Entropy Constant
- Hard Square Entropy Constant
- Hardy-Littlewood Conjectures
- Hardy-Littlewood Constants
- Hardy-Littlewood k-Tuple Conjecture