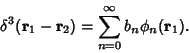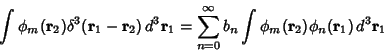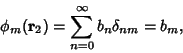| 释义 |
Green's FunctionLet
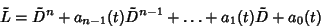 | (1) |
 Continuous for Continuous for  , 1, ..., , 1, ..., on the interval on the interval 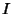 , and assume we wish to find the solution , and assume we wish to find the solution  to the equation to the equation
 | (2) |
 is a given Continuous on is a given Continuous on 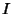 . To solve equation (2), we look for a function . To solve equation (2), we look for a function such that such that 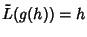 , where , where
 | (3) |
 | (4) |
 | (5) |
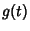 is called the Green's function for is called the Green's function for 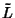 on on 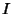 . .
Now, note that if we take 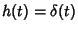 , then , then
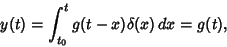 | (6) |
 | (7) |
For an arbitrary linear differential operator 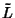 in 3-D, the Green's function in 3-D, the Green's function 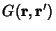 is defined byanalogy with the 1-D case by is defined byanalogy with the 1-D case by
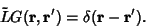 | (8) |
 is then is then
 | (9) |
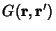 can often be found in terms of a basis of given eigenfunctions can often be found in terms of a basis of given eigenfunctions  by expandingthe Green's function by expandingthe Green's function
 | (10) |
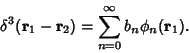 | (11) |
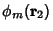 and integrating over and integrating over  space, space,
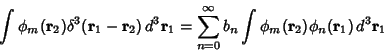 | (12) |
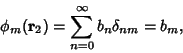 | (13) |
 | (14) |
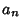 s, and substitutinginto s, and substitutinginto  , the original nonhomogeneous equation then can be solved. , the original nonhomogeneous equation then can be solved.
References
Arfken, G. ``Nonhomogeneous Equation--Green's Function,'' ``Green's Functions--One Dimension,'' and ``Green's Functions--Two and Three Dimensions.'' §8.7 and §16.5-16.6 in Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 480-491 and 897-924, 1985. |
![]() , then
, then![]() in 3-D, the Green's function
in 3-D, the Green's function ![]() is defined byanalogy with the 1-D case by
is defined byanalogy with the 1-D case by