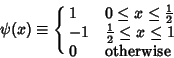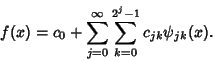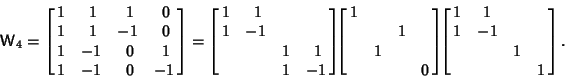| 释义 |
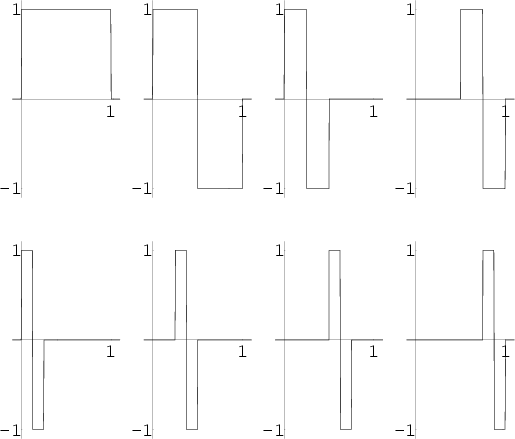
Haar FunctionDefine
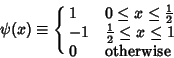 | (1) |
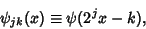 | (2) |
Then a Function 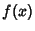 can be written as a series expansion by can be written as a series expansion by
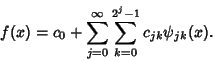 | (3) |
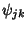 and and  are all Orthogonal in are all Orthogonal in 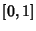 , with , with
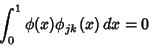 | (4) |
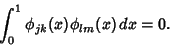 | (5) |
 intervals,with intervals,with  a Power of 2. Then an arbitrary function can be considered as an a Power of 2. Then an arbitrary function can be considered as an  -Vector -Vector 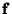 , and theCoefficients in the expansion , and theCoefficients in the expansion 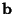 can be determined by solving the Matrix equation can be determined by solving the Matrix equation
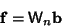 | (6) |
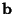 , where , where  is the Matrix of is the Matrix of  basis functions. For example, basis functions. For example,
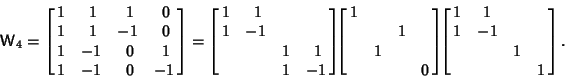 | (7) |
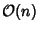 steps, compared to steps, compared to 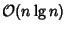 for theFourier Matrix.See also Wavelet, Wavelet Transform for theFourier Matrix.See also Wavelet, Wavelet Transform
References
Haar, A. ``Zur Theorie der orthogonalen Funktionensysteme.'' Math. Ann. 69, 331-371, 1910.Strang, G. ``Wavelet Transforms Versus Fourier Transforms.'' Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 28, 288-305, 1993. |