| 释义 |
Least Common MultipleThe least common multiple of two numbers 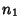 and and 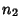 is denoted is denoted 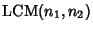 or or  and can be obtainedby finding the Prime factorization of each and can be obtainedby finding the Prime factorization of each
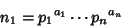 | (1) |
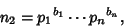 | (2) |
 s are all Prime Factors of s are all Prime Factors of 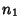 and and 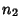 , and if , and if  does not occur in one factorization, then the corresponding exponent is 0. The least common multiple is then does not occur in one factorization, then the corresponding exponent is 0. The least common multiple is then
 | (3) |
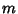 be a common multiple of be a common multiple of 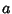 and and 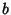 so that so that
 | (4) |
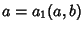 and and  , where , where 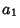 and and 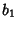 are Relatively Prime by definition of the GreatestCommon Divisor are Relatively Prime by definition of the GreatestCommon Divisor 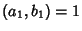 . Then . Then  , and from the Division Lemma (given that , and from the Division Lemma (given that  isDivisible by isDivisible by 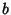 and and  ), we have ), we have 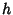 is Divisible by is Divisible by 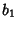 , so , so
 | (5) |
 | (6) |
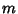 is given by is given by 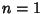 , ,
 | (7) |
 | (8) |
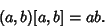 | (9) |
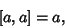 | (10) |
 | (11) |
 | (12) |
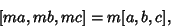 | (13) |
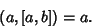 | (14) |
 | (15) |
References
Guy, R. K. ``Density of a Sequence with L.C.M. of Each Pair Less than  .'' §E2 in Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 200-201, 1994. .'' §E2 in Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 200-201, 1994.
|
![]() and
and ![]() is denoted
is denoted ![]() or
or ![]() and can be obtainedby finding the Prime factorization of each
and can be obtainedby finding the Prime factorization of each
![]() .'' §E2 in Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 200-201, 1994.
.'' §E2 in Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 200-201, 1994.