The three angle bisectors of a triangle are
CON
-
CURRENT
.
An excircle for a triangle is a circle that lies outside
the triangle and is tangent to one side of the triangle
and tangent to extensions of the remaining two sides. A
triangle has three distinct excircles.
In a more general context, if it is possible to draw a
circle inside a
POLYGON
tangent to each side of the poly-
gon, then that circle is called an incircle of the polygon.
Every regular polygon has an incircle. There is no incir-
cle for a nonsquare rectangle.
See also
CIRCUMCIRCLE
.
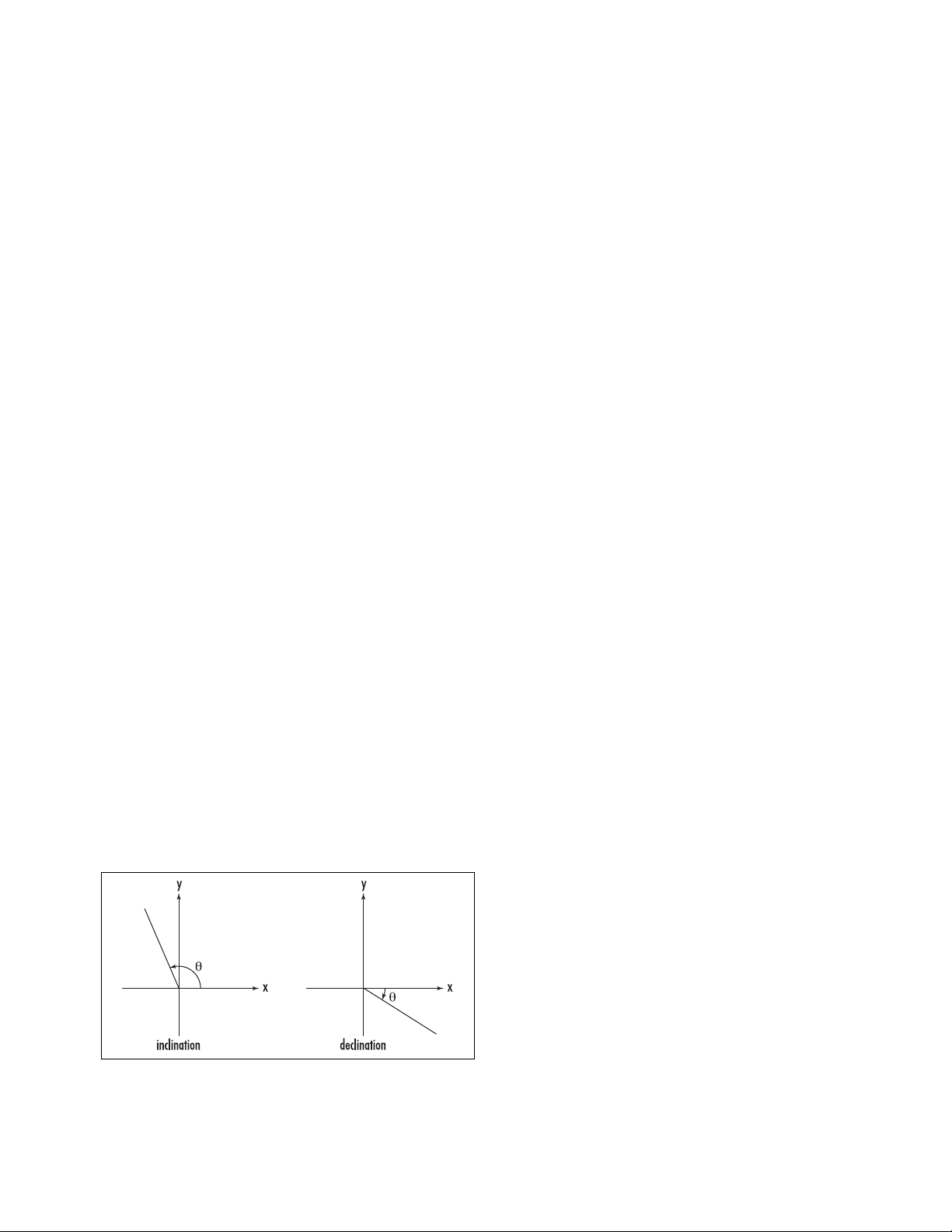
inclination/declination The angle θbetween a ray
emanating from the origin of a C
ARTESIAN COORDI
-
NATE
system and the positive x-axis as measured in an
anticlockwise direction is called the inclination of the
ray. An angle measured in the clockwise direction is
called its declination. These terms are rarely used in
mathematics today.
A
PLANE
that is not horizontal is called an inclined
plane, and the angle that the line of greatest slope
within the plane makes with the horizontal is called the
angle of inclination of the plane.
inclusion-exclusion principle If n(A) denotes the
number of elements in a finite set A, then the number
of elements in the union A∪Bof two sets is given by:
n(A∪B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A∩B)
(Counting the number of elements in each of Aand B
counts the elements that belong to both twice. One must
compensate for this double count.) Similarly, the number
of elements in the union of three sets is given by:
n(A∪B∪C) = n(A) + n(B) + n(C)
–n(A∩B) – n(B∩C)
– n(A∩C+ n(A∩B∩C)
(One can establish this either by reasoning through
which elements are counted multiple times, or by not-
ing that A∪B∪C= (A∪B) ∪Cand applying the
previous observation:
n((A∪B) ∪C) = n(A∪B) + n(C) – n((A∪B) ∩C)
= n(A∪B) + n(C) – n((A∩C) ∪(B∩C))
Two more applications of the formula for the union of
two give the result.)
In general, an
INDUCTION
argument shows that the
number of elements in the union of nsets is given by:
n(A1∪A2∪…∪Ak) = n(A1) + n(A2+…+ n(Ak)
–n(A1∩A2) – n(A1∩A3) –…
– n(Ak–1 ∩Ak)
+ n(A1∩A2∩A3) +…
+ n(Ak–2 ∩Ak–1 ∩Ak
+ (–1)kn(A1∩A2∩…∩Ak)
This formula is called the general inclusion-exclusion
principle. It can be interpreted as follows:
The number of elements of a finite set that pos-
sess at least one of kpossible properties is equal
to the number possessing exactly one property,
minus the number possessing exactly two prop-
erties, plus the number possessing precisely
three properties, and so on, up to the count of
those elements possessing all kproperties.
This powerful counting principle has important appli-
cations in
PROBABILITY
theory.
increasing/decreasing A
SEQUENCE
of numbers {an}
is said to be increasing if a1≤a2≤a3≤…, that is, each
term in the sequence is greater than or equal to the one
that precedes it. It is called strictly increasing if a1< a2
< a3< … The constant sequence 1,1,1, …, for example,
is considered increasing.
…
increasing/decreasing 261
Angles of inclination and declination