angular velocity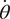 , where a dot denotes differentiation with respect to time.
, where a dot denotes differentiation with respect to time.
At a more advanced level, the angular velocity ω of the particle P is the vector defined by ω = θ˙ k, where i and j are unit vectors in the directions of the positive x- and y-axes, and k = i × j. If r and v are the position vector and velocity of P, then
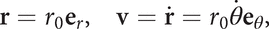
where er = i cos θ + j sin θ and eθ =−i sinθ + j cos θ (see circular motion). By using the fact that k = er × eθ, it follows that the velocity v is given by v = ω × r.
Consider a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis, and take coordinate axes so that the z-axis is along the fixed axis. Let (r0, θ) be the polar coordinates of some point of the rigid body, not on the axis, lying in the plane z =0. Then the angular velocity ω of the rigid body is defined by 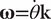 .
.
In general, for a rigid body that is rotating, such as a top spinning about a fixed point, the rigid body possesses an angular velocity ω whose magnitude and direction depend on time, though the formula v = ω × r still applies.
- perpendicular planes
- Perron's paradox
- perspective
- perspectivity
- perturbation
- peta-
- pgf
- p-group
- phase
- phase plane
- philosophy of mathematics
- pi
- Picard's little theorem
- Picard's theorem
- Pick's theorem
- pico-
- PID
- piecewise continuous
- pie chart
- pigeonhole principle
- pilot survey
- pivot
- pivot table
- placebo
- place value