hyperbola
The line through F1 and F2 is the transverse axis, and the points V1 and V2 where it cuts the hyperbola are the vertices. The length |V1V2| is the length of the transverse axis and is usually taken to be 2a. The midpoint of V1V2 is the centre of the hyperbola. The line through the centre perpendicular to the transverse axis is the conjugate axis. It is usual to introduce b (>0) defined by b2 = a2(e2−1), so that e2=1 + b2/a2. The two separate parts of the hyperbola are the two branches.
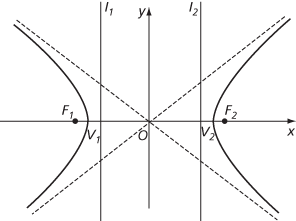
A hyperbola in normal form
If a coordinate system is taken with origin at the centre of the hyperbola, and x‐axis along the transverse axis, the foci have coordinates (ae, 0) and (−ae, 0), the directrices have equations x = a/e and x = −a/e, and the hyperbola's equation has the normal form

The hyperbola can be parametrized by x = asecθ, y = btanθ (0 ≤ θ<2π, θ ≠ π/2, 3π/2) or alternatively by x = acosh t, y = bsinht (tϵR) (see hyperbolic function), but this gives only one branch of the hyperbola.
The hyperbola, in normal form, has two asymptotes, y = (b/a)x and y = (−b/a)x. The shape of the hyperbola is determined by the eccentricity. The particular value 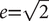 is important for this gives b = a. Then the asymptotes are perpendicular, and the hyperbola is called a rectangular hyperbola.
is important for this gives b = a. Then the asymptotes are perpendicular, and the hyperbola is called a rectangular hyperbola.
- Cauchy sequence
- Cauchy's formula for derivatives
- Cauchy's integral formula
- Cauchy's Integral Theorem
- Cauchy's mean value theorem
- Cauchy's Residue Theorem
- Cauchy's test
- Cauchy's Theorem
- Cauchy's Theorem
- Cauchy–Riemann equations
- Cauchy–Schwarz inequality
- Cauchy–Schwarz inequality for integrals
- Cauchy–Schwarz inequality for sums
- causation
- Cavalieri, Bonaventura
- Cayley, Arthur
- Cayley Representation Theorem
- Cayley's Theorem
- Cayley table
- Cayley–Hamilton Theorem
- cdf
- ceiling
- Celsius
- centesimal
- centi-