| 释义 |
Sinc FunctionA function also called the Sampling Function and defined by
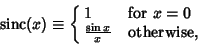 | (1) |
 is the Sine function. Let is the Sine function. Let  be the Rectangle Function, then the Fourier Transform of be the Rectangle Function, then the Fourier Transform of  is the sinc function is the sinc function
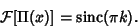 | (2) |
 as the so-called Instrument Function, which gives the instrumentalresponse to a Delta Function input. Removing the instrument functions from the final spectrum requires use of somesort of Deconvolution algorithm. as the so-called Instrument Function, which gives the instrumentalresponse to a Delta Function input. Removing the instrument functions from the final spectrum requires use of somesort of Deconvolution algorithm.
The sinc function can be written as a complex Integral by noting that
The sinc function can also be written as the Infinite Product
 | (4) |
These are all special cases of the amazing general result
 | (10) |
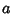 and and  are Positive integers such that are Positive integers such that 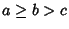 , ,  , , 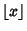 is the Floor Function,and is the Floor Function,and 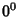 is taken to be equal to 1 (Kogan). This spectacular formula simplifies in the special case when is taken to be equal to 1 (Kogan). This spectacular formula simplifies in the special case when 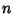 is a PositiveEven integer to is a PositiveEven integer to
 | (11) |
 is an Eulerian Number (Kogan). The solution of the integral can also be written in terms of theRecurrence Relation for the coefficients is an Eulerian Number (Kogan). The solution of the integral can also be written in terms of theRecurrence Relation for the coefficients
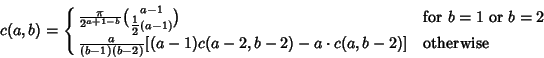 | (12) |
The half-infinite integral of 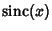 can be derived using Contour Integration.In the above figure, consider the path can be derived using Contour Integration.In the above figure, consider the path 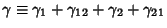 . Now write . Now write  . On an arc, . On an arc,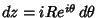 and on the x-Axis, and on the x-Axis, 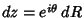 . Write . Write
 | (13) |
 denotes the Imaginary Point. Now define denotes the Imaginary Point. Now define
where the second and fourth terms use the identities  and and 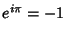 . Simplifying, . Simplifying,
where the third term vanishes by Jordan's Lemma. Performing the integration of the first term and combining theothers yield
 | (16) |
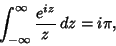 | (17) |
 | (18) |
so
 | (20) |
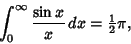 | (21) |
 | (22) |
An interesting property of 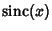 is that the set of Local Extrema of is that the set of Local Extrema of 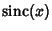 correspondsto its intersections with the Cosine function correspondsto its intersections with the Cosine function 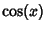 , as illustrated above. , as illustrated above. See also Fourier Transform, Fourier Transform--Rectangle Function,Instrument Function, Jinc Function, Sine, Sine Integral
References
Kogan, S. ``A Note on Definite Integrals Involving Trigonometric Functions.'' http://www.mathsoft.com/asolve/constant/pi/sin/sin.html.Morrison, K. E. ``Cosine Products, Fourier Transforms, and Random Sums.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 102, 716-724, 1995.
|


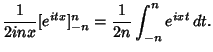


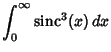




![]() can be derived using Contour Integration.In the above figure, consider the path
can be derived using Contour Integration.In the above figure, consider the path ![]() . Now write
. Now write ![]() . On an arc,
. On an arc,![]() and on the x-Axis,
and on the x-Axis, ![]() . Write
. Write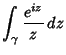





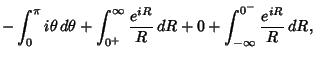

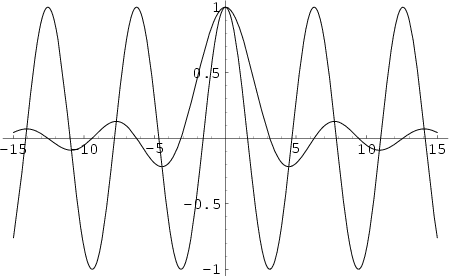
![]() is that the set of Local Extrema of
is that the set of Local Extrema of ![]() correspondsto its intersections with the Cosine function
correspondsto its intersections with the Cosine function ![]() , as illustrated above.
, as illustrated above.