Block Design
An incidence system (![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ) in which a set
) in which a set ![]() of
of ![]() points is partitioned into a family
points is partitioned into a family ![]() of
of![]() subsets (blocks) in such a way that any two points determine
subsets (blocks) in such a way that any two points determine ![]() blocks with
blocks with ![]() points in each block, andeach point is contained in
points in each block, andeach point is contained in ![]() different blocks. It is also generally required that
different blocks. It is also generally required that ![]() , which is where the``incomplete'' comes from in the formal term most often encountered for block designs, Balanced Incomplete BlockDesigns (BIBD). The five parameters are not independent, but satisfy the two relations
, which is where the``incomplete'' comes from in the formal term most often encountered for block designs, Balanced Incomplete BlockDesigns (BIBD). The five parameters are not independent, but satisfy the two relations
| (1) |
| (2) |
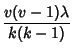 | (3) | ||
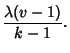 | (4) |
A BIBD is called Symmetric if
Writing ![]() and
and ![]() , then the Incidence Matrix of the BIBD is given by the
, then the Incidence Matrix of the BIBD is given by the ![]() Matrix
Matrix ![]() defined by
defined by
| (5) |
| (6) |
Examples of BIBDs are given in the following table.
| Block Design | ( |
| Affine Plane | ( |
| Fano Plane | (7, 3, 1)) |
| Hadamard Design | Symmetric ( |
| Projective Plane | Symmetric ( |
| Steiner Triple System | ( |
| Unital | ( |
References
Dinitz, J. H. and Stinson, D. R. ``A Brief Introduction to Design Theory.'' Ch. 1 in Contemporary Design Theory: A Collection of Surveys (Ed. J. H. Dinitz and D. R. Stinson). New York: Wiley, pp. 1-12, 1992. Ryser, H. J. ``The ![]() -Configuration.'' §8.1 in Combinatorial Mathematics. Buffalo, NY: Math. Assoc. Amer., pp. 96-102, 1963.
-Configuration.'' §8.1 in Combinatorial Mathematics. Buffalo, NY: Math. Assoc. Amer., pp. 96-102, 1963.
- Rayleigh-Ritz Variational Technique
- Rayleigh's Formulas
- Rayleigh's Theorem
- Real Analysis
- Real Axis
- Real Function
- Realizer
- Real Line
- Real Matrix
- Real Number
- Real Part
- Real Polynomial
- Real Projective Plane
- Real Quadratic Field
- Rearrangement Theorem
- Reciprocal
- Reciprocal Difference
- Reciprocal Polyhedron
- Reciprocating Sphere
- Reciprocation
- Reciprocity Theorem
- Rectangle
- Rectangle Function
- Rectangle Squaring
- Rectangular Coordinates