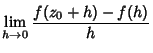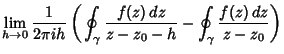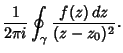| 释义 |
Cauchy Integral FormulaGiven a Contour Integral of the form
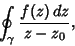 | (1) |
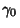 as an infinitesimal Circle around the point as an infinitesimal Circle around the point 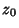 (the dot in the above illustration).Define the path (the dot in the above illustration).Define the path 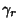 as an arbitrary loop with a cut line (on which the forward and reverse contributions canceleach other out) so as to go around as an arbitrary loop with a cut line (on which the forward and reverse contributions canceleach other out) so as to go around 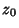 . .
The total path is then
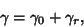 | (2) |
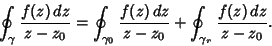 | (3) |
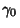 does not enclose the Pole, and we are leftwith does not enclose the Pole, and we are leftwith
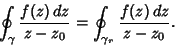 | (4) |
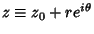 , so , so 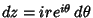 . Then . Then
But we are free to allow the radius  to shrink to 0, so to shrink to 0, so
and
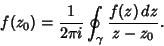 | (7) |
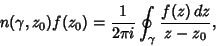 | (8) |
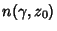 is the Winding Number. is the Winding Number.
A similar formula holds for the derivatives of  , ,
Iterating again,
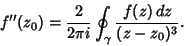 | (10) |
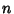 , ,
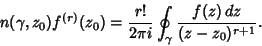 | (11) |
References
Arfken, G. ``Cauchy's Integral Formula.'' §6.4 in Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 371-376, 1985.Morse, P. M. and Feshbach, H. Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 367-372, 1953.
|
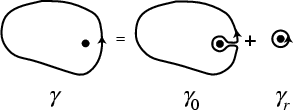
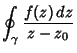
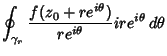
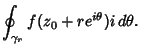
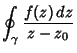
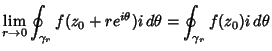
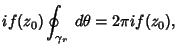
![]() ,
,