Surface Area
Surface area is the Area of a given surface. Roughly speaking, it is the ``amount'' of a surface,and has units of distance squares. It is commonly denoted ![]() for a surface in 3-D, or
for a surface in 3-D, or ![]() for a region ofthe plane (in which case it is simply called ``the'' Area).
for a region ofthe plane (in which case it is simply called ``the'' Area).
If the surface is Parameterized using ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then
| (1) |
The surface area given by rotating the curve ![]() from
from ![]() to
to ![]() about the
about the ![]() -axis is
-axis is
| (2) |
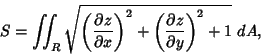 | (3) |
The following tables gives surface areas for some common Surfaces. In the first table, ![]() denotes thelateral surface, and in the second,
denotes thelateral surface, and in the second, ![]() denotes the total surface. In both tables,
denotes the total surface. In both tables, ![]() denotes the Radius,
denotes the Radius, ![]() theheight,
theheight, ![]() the base Perimeter, and
the base Perimeter, and ![]() the Slant Height (Beyer 1987).
the Slant Height (Beyer 1987).
| Surface | |
| Cone | |
| Conical Frustum | |
| Cube | |
| Cylinder | |
| Lune (Solid) | |
| Oblate Spheroid | |
| Prolate Spheroid | |
| Pyramid | |
| Pyramidal Frustum | |
| Sphere | |
| Torus | |
| Zone |
| Surface | |
| Cone | |
| Conical Frustum | |
| Cylinder |
Even simple surfaces can display surprisingly counterintuitive properties. For instance, the surface of revolution of ![]() around the x-Axis for
around the x-Axis for ![]() is called Gabriel's Horn, and has Finite Volume butInfinite surface Area.
is called Gabriel's Horn, and has Finite Volume butInfinite surface Area.
References
Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 28th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 127-132, 1987.
- Feuerbach's Theorem
- Feynman Point
- FFT
- Fiber
- Fiber Bundle
- Fiber Space
- Fibonacci Dual Theorem
- Fibonacci Hyperbolic Cosine
- Fibonacci Hyperbolic Cotangent
- Fibonacci Hyperbolic Sine
- Fibonacci Hyperbolic Tangent
- Fibonacci Identity
- Fibonacci Matrix
- Fibonacci n-Step Number
- Fibonacci Number
- Fibonacci Polynomial
- Fibonacci Pseudoprime
- Fibonacci Q-Matrix
- Fibonacci Sequence
- Fibration
- Field
- Field Axioms
- Field Extension
- Fields Medal
- Fifteen Theorem