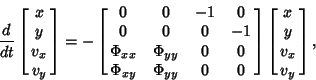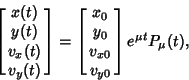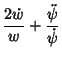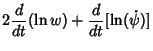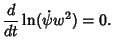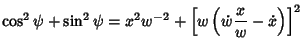| 释义 |
Floquet AnalysisGiven a system of periodic Ordinary Differential Equations of the form
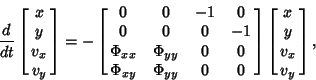 | (1) |
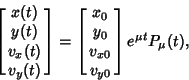 | (2) |
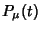 is a function periodic with the same period is a function periodic with the same period  as the equations themselves. Given an OrdinaryDifferential Equation of the form as the equations themselves. Given an OrdinaryDifferential Equation of the form
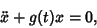 | (3) |
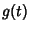 is periodic with period is periodic with period  , the ODE has a pair of independent solutions given by the Real and Imaginary Parts of , the ODE has a pair of independent solutions given by the Real and Imaginary Parts of
Plugging these into (3) gives
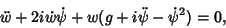 | (7) |
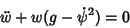 | (8) |
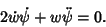 | (9) |
Integrating gives
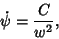 | (11) |
 is a constant which must equal 1, so is a constant which must equal 1, so 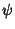 is given by is given by
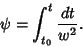 | (12) |
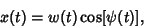 | (13) |
and
which is an integral of motion. Therefore, although 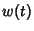 is not explicitly known, an integral is not explicitly known, an integral  always exists.Plugging (10) into (8) gives always exists.Plugging (10) into (8) gives
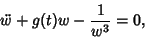 | (16) |
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.). Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing. New York: Dover, p. 727, 1972.Binney, J. and Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, p. 175, 1987. Lichtenberg, A. and Lieberman, M. Regular and Stochastic Motion. New York: Springer-Verlag, p. 32, 1983. Margenau, H. and Murphy, G. M. The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, 2 vols. Princeton, NJ: Van Nostrand, 1956-64. Morse, P. M. and Feshbach, H. Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 556-557, 1953.
|