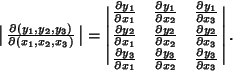| 释义 |
JacobianGiven a set  of of  equations in equations in  variables variables 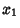 , ..., , ...,  , written explicitly as , written explicitly as
 | (1) |
 | (2) |
 | (3) |
 is the Jacobian Determinant (confusingly, often called ``the Jacobian'' as well)and is denoted is the Jacobian Determinant (confusingly, often called ``the Jacobian'' as well)and is denoted
 | (4) |
Taking the differential
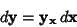 | (5) |
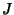 is the Determinant of the Matrix is the Determinant of the Matrix 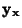 , and therefore gives the ratios of , and therefore gives the ratios of  -Dvolumes (Contents) in -Dvolumes (Contents) in  and and 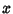 , ,
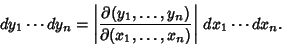 | (6) |
 functions in more than functions in more than  variables. For example, considering variables. For example, considering and and 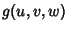 , the Jacobians , the Jacobians
can be defined (Kaplan 1984, p. 99).
For the case of  variables, the Jacobian takes the special form variables, the Jacobian takes the special form
 | (9) |
 is the Dot Product and is the Dot Product and 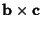 is the Cross Product,which can be expanded to give is the Cross Product,which can be expanded to give
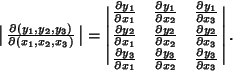 | (10) |
References
Kaplan, W. Advanced Calculus, 3rd ed. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, pp. 98-99, 123, and 238-245, 1984.Simon, C. P. and Blume, L. E. Mathematics for Economists. New York: W. W. Norton, 1994. |
![]() of
of ![]() equations in
equations in ![]() variables
variables ![]() , ...,
, ..., ![]() , written explicitly as
, written explicitly as



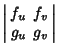

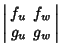
![]() variables, the Jacobian takes the special form
variables, the Jacobian takes the special form