Logarithmic Spiral
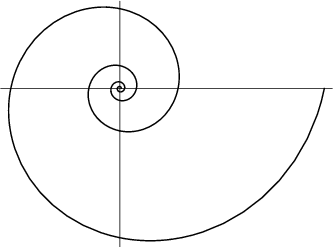
A curve whose equation in Polar Coordinates is given by
| (1) |
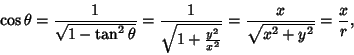 | (2) |
| (3) | |||
| (4) |
The logarithmic spiral was first studied by Descartes ![]() in 1638 and Jakob Bernoulli.
in 1638 and Jakob Bernoulli. ![]() Bernoulli was so fascinated by the spiral that he had one engraved on his tombstone (althoughthe engraver did not draw it true to form). Torricelli worked on it independently and found the length of the curve(MacTutor Archive).
Bernoulli was so fascinated by the spiral that he had one engraved on his tombstone (althoughthe engraver did not draw it true to form). Torricelli worked on it independently and found the length of the curve(MacTutor Archive).
The rate of change of Radius is
| (5) |
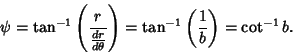 | (6) |
If ![]() is any point on the spiral, then the length of the spiral from
is any point on the spiral, then the length of the spiral from ![]() to the origin is finite. In fact, from the point
to the origin is finite. In fact, from the point ![]() which is at distance
which is at distance ![]() from the origin measured along a Radius vector, the distance from
from the origin measured along a Radius vector, the distance from ![]() to the Pole alongthe spiral is just the Arc Length. In addition, any Radius from the origin meets the spiral at distances which arein MacTutor Archive).
to the Pole alongthe spiral is just the Arc Length. In addition, any Radius from the origin meets the spiral at distances which arein MacTutor Archive).

The Arc Length, Curvature, and Tangential Angle of the logarithmic spiral are
 | |||
 | (7) | ||
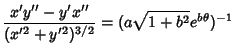 | (8) | ||
 | (9) |
The Cesàro Equation is
| (10) |
References
Lawrence, J. D. A Catalog of Special Plane Curves. New York: Dover, pp. 184-186, 1972. Lee, X. ``EquiangularSpiral.''http://www.best.com/~xah/SpecialPlaneCurves_dir/EquiangularSpiral_dir/equiangularSpiral.html Lockwood, E. H. ``The Equiangular Spiral.'' Ch. 11 in A Book of Curves. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, pp. 98-109, 1967. MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. ``Equiangular Spiral.''http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/Curves/Equiangular.html.
- Vector Integral
- Vector Norm
- Vector Ordering
- Vector Potential
- Vector Quadruple Product
- Vector Space
- Vector Spherical Harmonic
- Vector Transformation Law
- Vector Triple Product
- Vee
- Velocity
- Venn Diagram
- Verging Construction
- Verhulst Model
- Veronese Surface
- Veronese Variety
- Versed Sine
- Versiera
- Versine
- Vertex Angle
- Vertex Coloring
- Vertex Connectivity
- Vertex Cover
- Vertex Degree
- Vertex Enumeration