Lusin's Theorem
Let ![]() be a finite and Measurable Function in
be a finite and Measurable Function in ![]() , and let
, and let ![]() be freely chosen. Then there is a function
be freely chosen. Then there is a function![]() such that
such that
- 1.
 is continuous in
is continuous in 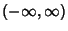 ,
, - 2. The Measure of
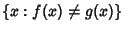 is
is 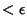 ,
, - 3.
 ,
,
References
Kestelman, H. §4.4 in Modern Theories of Integration, 2nd rev. ed. New York: Dover, pp. 30 and 109-112, 1960.
- Great Dodecicosahedron
- Great Dodecicosidodecahedron
- Greater
- Greater Than/Less Than Symbol
- Greatest Common Denominator
- Greatest Common Divisor
- Greatest Common Divisor Theorem
- Greatest Common Factor
- Greatest Integer Function
- Greatest Lower Bound
- Greatest Prime Factor
- Great Hexacronic Icositetrahedron
- Great Hexagonal Hexecontahedron
- Great Icosacronic Hexecontahedron
- Great Icosahedron
- Great Icosahedron-Great Stellated Dodecahedron Compound
- Great Icosicosidodecahedron
- Great Icosidodecahedron
- Great Icosihemidodecacron
- Great Icosihemidodecahedron
- Great Inverted Pentagonal Hexecontahedron
- Great Inverted Retrosnub Icosidodecahedron
- Great Inverted Snub Icosidodecahedron
- Great Pentagonal Hexecontahedron
- Great Pentagrammic Hexecontahedron