| 释义 |
Bayes' FormulaLet 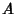 and and  be Sets. Conditional Probability requires that be Sets. Conditional Probability requires that
 | (1) |
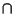 denotes Intersection (``and''), and also that denotes Intersection (``and''), and also that
 | (2) |
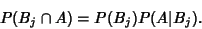 | (3) |
 | (4) |
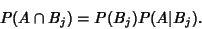 | (5) |
 | (6) |
 | (7) |
 | (8) |
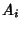 is an event in is an event in  and and  for for  , then , then
 | (9) |
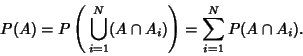 | (10) |
 | (11) |
 | (12) |
References
Press, W. H.; Flannery, B. P.; Teukolsky, S. A.; and Vetterling, W. T. Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, p. 810, 1992.
|
![]() and
and ![]() be Sets. Conditional Probability requires that
be Sets. Conditional Probability requires that