| 释义 |
Standard MapA 2-D Map, also called the Taylor-Greene-Chirikov Map in some of the older literature.
where  and and  are computed mod are computed mod 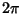 and and  is a Positive constant. An analytic estimate of the width of theChaotic zone (Chirikov 1979) finds is a Positive constant. An analytic estimate of the width of theChaotic zone (Chirikov 1979) finds
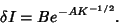 | (3) |
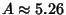 and and  . The value of . The value of  at which global Chaos occurs has been bounded by various authors. Greene's Method is the most accurate method so far devised. at which global Chaos occurs has been bounded by various authors. Greene's Method is the most accurate method so far devised.| Author | Bound | Fraction | Decimal | | Hermann | 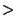 |  | 0.029411764 | | Italians | 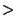 | - | 0.65 | | Greene |  | - | 0.971635406 | | MacKay and Pearson | 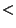 | 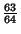 | 0.984375000 | | Mather | 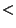 | 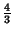 | 1.333333333 |
Fixed Points are found by requiring that
The first gives  , so , so  and and
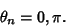 | (6) |
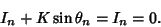 | (7) |
 and and 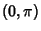 . In order to perform a Linear Stability analysis, take differentials of the variables . In order to perform a Linear Stability analysis, take differentials of the variables
In Matrix form,
 | (10) |
 | (11) |
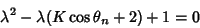 | (12) |
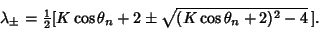 | (13) |
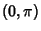 , ,
The Fixed Point will be stable if  Here, that means Here, that means
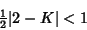 | (15) |
 | (16) |
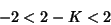 | (17) |
 | (18) |
 . For the Fixed Point (0, 0), the Eigenvalues are . For the Fixed Point (0, 0), the Eigenvalues are
If the map is unstable for the larger Eigenvalue, it is unstable. Therefore, examine  . We have . We have
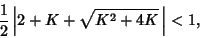 | (20) |
 | (21) |
 | (22) |
 , so the second part of the inequality cannot be true. Therefore, the map is unstable at the FixedPoint (0, 0). , so the second part of the inequality cannot be true. Therefore, the map is unstable at the FixedPoint (0, 0).
References
Chirikov, B. V. ``A Universal Instability of Many-Dimensional Oscillator Systems.'' Phys. Rep. 52, 264-379, 1979.
|

