Circumcenter
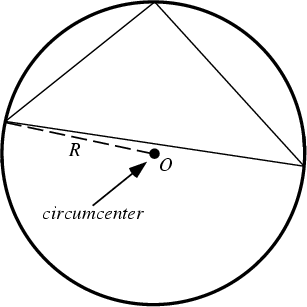
The center ![]() of a Triangle's Circumcircle. It can be found as the intersection of thePerpendicular Bisectors. If the Triangle is Acute,the circumcenter is in the interior of the Triangle. In a Right Triangle, the circumcenter is theMidpoint of the Hypotenuse.
of a Triangle's Circumcircle. It can be found as the intersection of thePerpendicular Bisectors. If the Triangle is Acute,the circumcenter is in the interior of the Triangle. In a Right Triangle, the circumcenter is theMidpoint of the Hypotenuse.
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
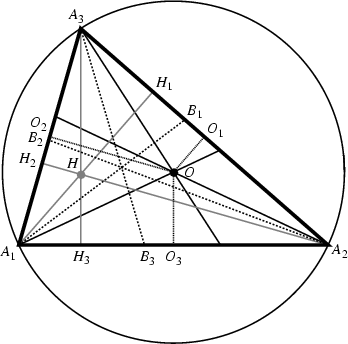
The circumcenter ![]() and Orthocenter
and Orthocenter ![]() are Isogonal Conjugates.
are Isogonal Conjugates.
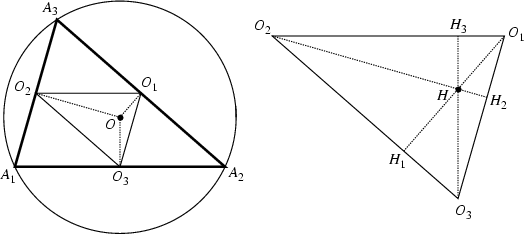
The Orthocenter ![]() of the Pedal Triangle
of the Pedal Triangle ![]() formed by the Circumcenter
formed by the Circumcenter ![]() concurs with the circumcenter
concurs with the circumcenter ![]() itself, as illustrated above. The circumcenter also lies on the Euler Line.
itself, as illustrated above. The circumcenter also lies on the Euler Line.
References
Carr, G. S. Formulas and Theorems in Pure Mathematics, 2nd ed. New York: Chelsea, p. 623, 1970. Dixon, R. Mathographics. New York: Dover, p. 55, 1991. Eppstein, D. ``Circumcenters of Triangles.''http://www.ics.uci.edu/~eppstein/junkyard/circumcenter.html. Johnson, R. A. Modern Geometry: An Elementary Treatise on the Geometry of the Triangle and the Circle. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 1929. Kimberling, C. ``Central Points and Central Lines in the Plane of a Triangle.'' Math. Mag. 67, 163-187, 1994. Kimberling, C. ``Circumcenter.''http://cedar.evansville.edu/~ck6/tcenters/class/ccenter.html.
- Zeckendorf Representation
- Zeckendorf's Theorem
- Zeeman's Paradox
- Zeilberger's Algorithm
- Zeisel Number
- Zeno's Paradoxes
- Zermelo-Fraenkel Axioms
- Zermelo-Fraenkel Set Theory
- Zermelo's Axiom of Choice
- Zermelo Set Theory
- Zernike Polynomial
- Zero
- Zero Divisor
- Zero (Root)
- Zero-Sum Game
- Zeta Fuchsian
- Zeta Function
- Zeuthen's Rule
- Zeuthen's Theorem
- Zig Number
- Zigzag Permutation
- Zig-Zag Triangle
- Zillion
- Zipf's Law
- Z-Number