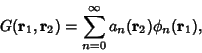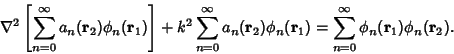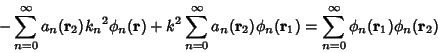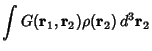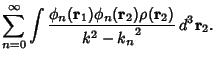| 释义 |
Green's Function--Helmholtz Differential EquationThe inhomogeneous Helmholtz Differential Equation is
 | (1) |
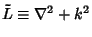 . The Green's function is then defined by . The Green's function is then defined by
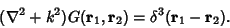 | (2) |
 as the solutions to the homogeneous Helmholtz Differential Equation as the solutions to the homogeneous Helmholtz Differential Equation
 | (3) |
 s, s,
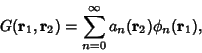 | (4) |
 | (5) |
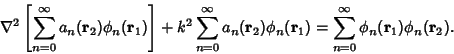 | (6) |
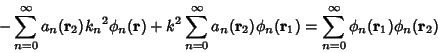 | (7) |
 | (8) |
 , so , so
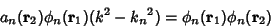 | (9) |
 | (10) |
 | (11) |
References
Arfken, G. Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 529-530, 1985. |