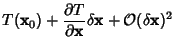| 释义 |
Linear StabilityConsider the general system of two first-order Ordinary Differential Equations
Let 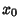 and and  denote Fixed Points with denote Fixed Points with 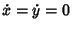 , so , so
Then expand about  so so
To first-order, this gives
 | (7) |
 Matrix is called the Stability Matrix. Matrix is called the Stability Matrix.
In general, given an 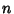 -D Map -D Map 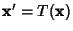 , let , let  be a Fixed Point, so that be a Fixed Point, so that
 | (8) |
so
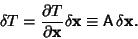 | (10) |
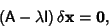 | (11) |
 | (12) |
 | (13) |
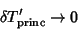 | (14) |
 for for  , ..., , ..., 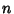 but but 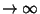 if any if any  . Analysis of theEigenvalues (and Eigenvectors) of A therefore characterizes the typeof Fixed Point. The condition for stability is . Analysis of theEigenvalues (and Eigenvectors) of A therefore characterizes the typeof Fixed Point. The condition for stability is  for for  , ..., , ..., 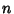 .See also Fixed Point, Stability Matrix .See also Fixed Point, Stability Matrix
References
Tabor, M. ``Linear Stability Analysis.'' §1.4 in Chaos and Integrability in Nonlinear Dynamics: An Introduction. New York: Wiley, pp. 20-31, 1989. |
![]() -D Map
-D Map ![]() , let
, let ![]() be a Fixed Point, so that
be a Fixed Point, so that