gradient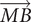 where the line through M and B has positive direction upwards. In other words, MB equals the length |MB| if B is above M, and equals −|MB| if B is below M. Similarly, AM = −|AM| if M is to the right of A, and AM = −|AM| if M is to the left of A. Two cases are illustrated in the figures.)
where the line through M and B has positive direction upwards. In other words, MB equals the length |MB| if B is above M, and equals −|MB| if B is below M. Similarly, AM = −|AM| if M is to the right of A, and AM = −|AM| if M is to the left of A. Two cases are illustrated in the figures.)
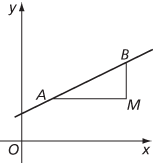
B is above A
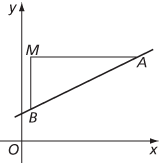
B is below A
The gradient of the line through A and B may be denoted by mAB, and, if A and B have coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), with x1 ≠ x2, then

Though defined in terms of two points A and B on the line, the gradient of the line is independent of the choice of A and B. The line in the figures has gradient  .
.
Alternatively, the gradient may be defined as equal to tanθ, where either direction of the line makes an angle θ with the positive x‐axis. (The different possible values for θ give the same value for tanθ.) If the line through A and B is vertical, that is, parallel to the y‐axis, it is customary to say that the gradient is infinite. The following properties hold:
- divisor
- divisor function
- divisor of zero
- dodecagon
- dodecahedron
- Dodgson, Charles Lutwidge
- domain
- domain
- domain
- dominated convergence theorem
- Donaldson, Simon
- dot
- dot product
- double dummy
- double factorial
- double integral
- double negation
- double point
- double precision
- double root
- double sequence
- double series
- double tangent
- double‐angle formula
- double‐angle formula