labelling algorithm
You can start with any flow, including the zero flow, where the flow on every edge is zero. Each edge should be labelled with both the current flow and the excess capacity along that edge. Choose a path from source to sink, and take the smallest of the flows along any of the edges on that path. On each edge, transfer that amount of flow from the current flow to the excess capacity. Now choose another path and repeat the process, and continue until no path can be found that does not have at least one edge with zero flow. This is often easy to see, as any cut with zero flow guarantees that no such path exists.
The excess capacities on each edge at this stage represent the maximum flow. Note that the maximum flow can often be achieved in a number of different ways, and the choice of a different order of paths from source to sink will often lead to a different network solution, but with the same maximum flow.
For example,
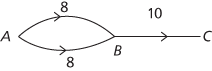
In this very simple network the maximum flow occurs when a total of 10 units flow along the two edges between A and B. However, any x satisfying 2 ≤ x ≤ 8 and 10−x along the two edges will be a maximum flow.
For the network shown here, an initial zero flow is shown in bold, so the excess capacity currently on each edge is the capacity of the edge.
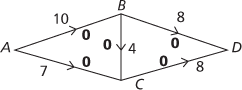
Starting with the path ABD the smallest flow on the route is 8, so transfer 8 to the excess capacity on both AB and BD.
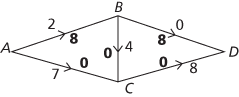
Now choose path ACD which has smallest flow 7, giving
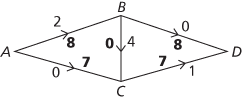
The only route left is ABCD with smallest flow 1, giving
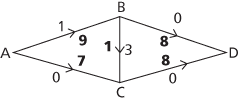
Since all routes into the sink at D have 0 excess capacity, it is obvious immediately that no further increases would be available and the maximum flow is 16, and the bold figures show a way of achieving this maximum flow. If ABCD had been chosen as the second path, before ACD, then 10 would have gone along AB, 2 along BC, and 6 along AC instead of this solution.
- ordinary differential equation
- ordinate
- orientable
- orientation
- origin
- orthocentre
- orthogonal
- orthogonal complement
- orthogonal curves
- orthogonal matrix
- orthogonal polynomials
- orthogonal projection
- orthogonal set
- orthonormal
- Osborne's rule
- oscillations
- osculate
- osculation
- osculinflection
- outer measure
- outer product
- outlier
- output
- p
- P