| 释义 |
Ordinary Differential Equation--System with Constant CoefficientsTo solve the system of differential equations
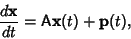 | (1) |
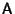 is a Matrix and is a Matrix and  and and 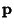 are Vectors, first consider the homogeneouscase with are Vectors, first consider the homogeneouscase with 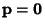 . Then the solutions to . Then the solutions to
 | (2) |
 | (3) |
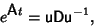 | (4) |
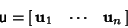 | (5) |
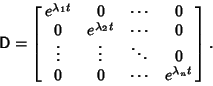 | (6) |
The individual solutions are then
 | (8) |
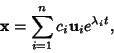 | (9) |
 s are arbitrary constants. s are arbitrary constants.
The general procedure is therefore - 1. Find the Eigenvalues of the Matrix
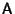 ( ( , ..., , ..., 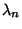 ) bysolving the Characteristic Equation. ) bysolving the Characteristic Equation. - 2. Determine the corresponding Eigenvectors
 , ..., , ..., 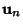 . . - 3. Compute
 | (10) |
 , ..., , ...,  . Then the Vectors . Then the Vectors 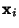 which are Real aresolutions to the homogeneous equation. If which are Real aresolutions to the homogeneous equation. If 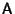 is a is a  matrix, the Complex vectors matrix, the Complex vectors correspond to Real solutions to the homogeneous equation given by correspond to Real solutions to the homogeneous equation given by 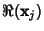 and and 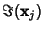 . . - 4. If the equation is nonhomogeneous, find the particular solution given by
 | (11) |
 is defined by is defined by
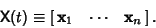 | (12) |
 , then look for a solution of the form , then look for a solution of the form
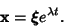 | (13) |
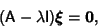 | (14) |
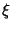 is an Eigenvector and is an Eigenvector and 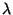 an Eigenvalue. an Eigenvalue. - 5. The general solution is
 | (15) |
|
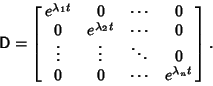

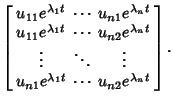
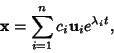
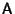 (
( , ...,
, ..., 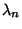 ) bysolving the Characteristic Equation.
) bysolving the Characteristic Equation. , ...,
, ..., 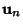 .
.
 , ...,
, ...,  . Then the Vectors
. Then the Vectors 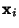 which are Real aresolutions to the homogeneous equation. If
which are Real aresolutions to the homogeneous equation. If 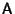 is a
is a  matrix, the Complex vectors
matrix, the Complex vectors correspond to Real solutions to the homogeneous equation given by
correspond to Real solutions to the homogeneous equation given by 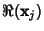 and
and 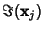 .
.
 is defined byIf the equation is homogeneous so that
is defined byIf the equation is homogeneous so that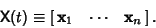
 , then look for a solution of the form This leads to an equation
, then look for a solution of the form This leads to an equation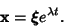
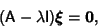
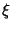 is an Eigenvector and
is an Eigenvector and 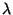 an Eigenvalue.
an Eigenvalue.