| 释义 |
Correlation DimensionDefine the correlation integral as
 | (1) |
 is the Heaviside Step Function. When the below limit exists, the correlation dimension is thendefined as is the Heaviside Step Function. When the below limit exists, the correlation dimension is thendefined as
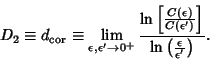 | (2) |
 is the Correlation Exponent, then is the Correlation Exponent, then
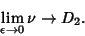 | (3) |
 | (4) |
To estimate the correlation dimension of an  -dimensional system with accuracy -dimensional system with accuracy  requires requires  data points, where data points, where
 | (5) |
 is the length of the ``plateau region.'' If an Attractorexists, then an estimate of is the length of the ``plateau region.'' If an Attractorexists, then an estimate of  saturates above some saturates above some  given by given by
 | (6) |
References
Nayfeh, A. H. and Balachandran, B. Applied Nonlinear Dynamics: Analytical, Computational, and Experimental Methods. New York: Wiley, pp. 547-548, 1995.
|

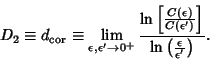
![]() -dimensional system with accuracy
-dimensional system with accuracy ![]() requires
requires ![]() data points, where
data points, where