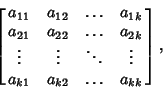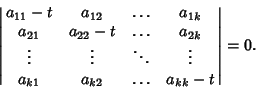| 释义 |
Characteristic EquationThe equation which is solved to find a Matrix's Eigenvalues, also called theCharacteristic Polynomial. Given a  system of equations with Matrix system of equations with Matrix
 | (1) |
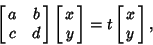 | (2) |
 | (3) |
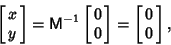 | (4) |
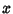 and and 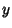 . Therefore, M has no inverse, so its Determinantis 0. This gives the characteristic equation . Therefore, M has no inverse, so its Determinantis 0. This gives the characteristic equation
 | (5) |
 denotes the Determinant of A. For a general denotes the Determinant of A. For a general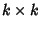 Matrix Matrix
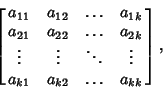 | (6) |
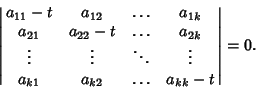 | (7) |
References
Gradshteyn, I. S. and Ryzhik, I. M. Tables of Integrals, Series, and Products, 5th ed. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, pp. 1117-1119, 1979.
|
![]() system of equations with Matrix
system of equations with Matrix