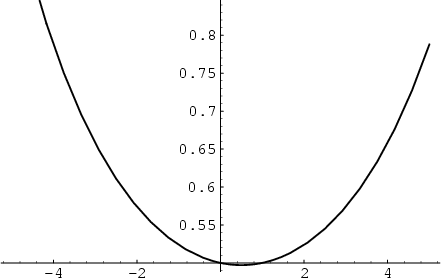
| 释义 |
Xi Function
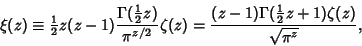 | (1) |
 is the Riemann Zeta Function and is the Riemann Zeta Function and 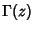 is the Gamma Function (Gradshteyn and Ryzhik1980, p. 1076). The is the Gamma Function (Gradshteyn and Ryzhik1980, p. 1076). The  function satisfies the identity function satisfies the identity
 | (2) |
 and of its Derivatives are all located on the Critical Strip and of its Derivatives are all located on the Critical Strip 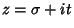 ,where ,where  . Therefore, the nontrivial zeros of the Riemann Zeta Function exactly correspond to those of . Therefore, the nontrivial zeros of the Riemann Zeta Function exactly correspond to those of  . The function . The function  is related to what Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (1980, p. 1074) call is related to what Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (1980, p. 1074) call 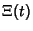 by by
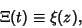 | (3) |
 . This function can also be defined as . This function can also be defined as
 | (4) |
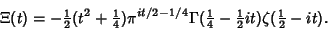 | (5) |
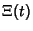 function.See also de Bruijn-Newman Constant function.See also de Bruijn-Newman Constant
References
Gradshteyn, I. S. and Ryzhik, I. M. Tables of Integrals, Series, and Products, corr. enl. 4th ed. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, 1980. |